History of removable prosthesis and the 3 Major lines
Who invented dentures?
This extraordinary solution, like the invention of the wheel, has ancient origins. Let's find out together!
Some history
Prosthetic restorations have originated since ancient times. The first dental bridges were invented by the Etruscans between 1.000 and 400 b.C. They connected gold rings with healthy teeth.

Denture-like artifacts were made using various materials including ivory, bone and even wood.
Human and ivory teeth were the most prestigious, but they met with rapid decay, also leaving a bitter taste in the mouth and smelly breath.
People in the upper classes of society could not accept having a toothless mouth, but the quality of the prostheses often prevented them from even eating, sometimes even speaking properly. The problems, besides being functional, were mainly due to the availability and price of teeth.
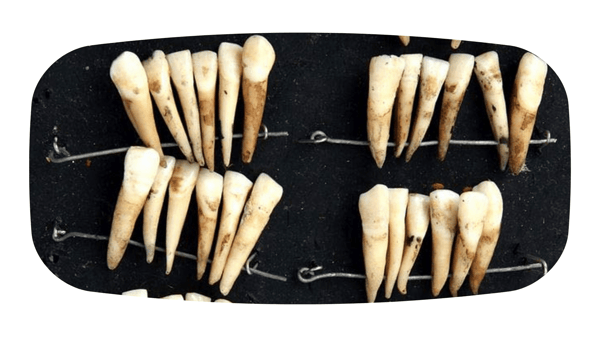 From the 1700s architects of the mouth began to use prostheses more widely made from human teeth extracted from corpses or 'sold out' by people from the lower classes. The poor were the usual source of supply for dentists and, despite availability, it was difficult to find good quality material because of the poor hygiene of the time.
From the 1700s architects of the mouth began to use prostheses more widely made from human teeth extracted from corpses or 'sold out' by people from the lower classes. The poor were the usual source of supply for dentists and, despite availability, it was difficult to find good quality material because of the poor hygiene of the time.
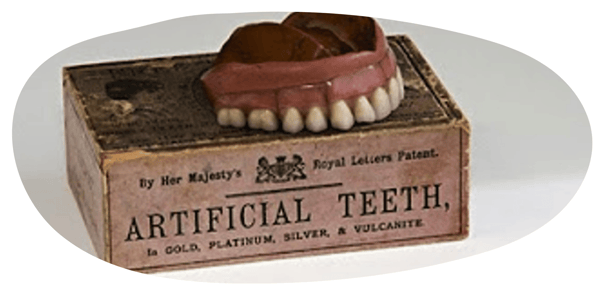
 In 1778 a pharmacist named Duchateau obtained the first patent for artificial teeth, made of porcelain, from French King Louis XVI.
In 1778 a pharmacist named Duchateau obtained the first patent for artificial teeth, made of porcelain, from French King Louis XVI.
However it was in March 1822 that the patent for the first artificial teeth in modern dentistry was celebrated by Charles Graham in New York.
Also in 1850, thanks to the invention of vulcanite, the first rudimentary mucous-supported dentures could be made. The use of vulcanite lowered the price of dentures by ⅔ compared to the gold base.
 Nel 1900, con l’avvento delle resine acriliche e i passi giganti effettuati dall’odontoiatria nello studio delle ricostruzioni nei pazienti con edentulia, tutto è cambiato: le tecnologie di nuova generazione hanno permesso di produrre materiale di alta qualità, ad un costo minore, accessibile a tutti.
Nel 1900, con l’avvento delle resine acriliche e i passi giganti effettuati dall’odontoiatria nello studio delle ricostruzioni nei pazienti con edentulia, tutto è cambiato: le tecnologie di nuova generazione hanno permesso di produrre materiale di alta qualità, ad un costo minore, accessibile a tutti.
Currently, despite the increasingly thoughtful use of CAD-CAM technology (discover the advantages of technology CAD-CAM compared with the traditional analog method), splint teeth are still the most widely used material in removable prosthetics Dentures integrated solution by 88dent(discover the All4Denture integrated solution by 88dent).
The 3 Major lines: PLUS, PLUS COMP and AF COMP
Major Plus: 4-layer PMMA teeth.
 The Plus line provides an important range in terms of the choice of shapes. The most recent one is exactly superimposable on the Comp and AF Comp from which it differs only in the choice of material used for their production, in the case of the Plus we are in fact talking about resin in 4 layers.
The Plus line provides an important range in terms of the choice of shapes. The most recent one is exactly superimposable on the Comp and AF Comp from which it differs only in the choice of material used for their production, in the case of the Plus we are in fact talking about resin in 4 layers.
Features:
- available colors v. A1-D4;
- 34 shapes ant. upper e 14 shapes ant. lower;
- technical posterior forms 20°, medium anatomical 23°-25°, high anatomical 25°, WFA - lingualized mounting.
Major Plus Comp: 4-layer PMMA & composite.
 The use of composite materials in the fabrication of artificial teeth has demonstrated a number of advantages over traditional acrylic resin teeth, such as high surface hardness, resistance to abrasion and compression, fracture, and perfect tooth stability even after grinding or curing of the prosthesis.
The use of composite materials in the fabrication of artificial teeth has demonstrated a number of advantages over traditional acrylic resin teeth, such as high surface hardness, resistance to abrasion and compression, fracture, and perfect tooth stability even after grinding or curing of the prosthesis.
These features ensure excellent long-term performance.
Major Plus Comp is a multilayer tooth with composite enamel layer, dentin and cervical layers made of acrylic PMMA material to ensure a perfect chemical bond with the denture base.
The enamel layer is made of composite material to ensure perfect protection of the teeth during chewing, dimensional stability and balance of the prosthesis to meet every requirement of modern prosthetic technique.
Major Plus Comp has excellent functional precision of occlusal profiles combined with modern, natural aesthetics.
Major Plus Comp teeth are designed to meet all technical and aesthetic requirements.
Features:
- available colours v. A1-D4;
- 10 shapes ant. upper S-M-B e 4 forme ant. L;
- technical posterior forms 20°, anatomical 23°-25°, WFA - lingualized mounting.
Major AF Comp: aesthetic veneers in PMMA & composite.
 Major AF Comp is a line of multilayer veneers made of composite material designed specifically for restorations and veneers.
Major AF Comp is a line of multilayer veneers made of composite material designed specifically for restorations and veneers.
Major AF Comp veneers can be used for a variety of restorative treatments, either directly in the dentist's office or in the dental technician's laboratory.
They are developed in combination with the Major AF Link system, a range of light-cured acrylic and composite products, for the creation and characterization of implant-supported prosthetic restorations with high functional esthetic value.
- available colours v. A1-D4;
- 10 shapes ant. upper S-M-B e 4 shapes ant. lower L;
- 2 shapes pos.R/L sup-lower. WFA, 1 shapes post. R/L sup-lower T, 1 shapes post.R/L sup-i
The rehabilitation pathway Major
Rehabilitation of total edentulism includes a wide range of treatment options.
- osteomucosal-supported prostheses (A);
- hybrid implant- and mucosal-supported solutions (B);
- total implant-supported rehabilitations (C).
In more complex cases, it is advisable to proceed in stages so that the aesthetic, functional, and compliance results obtained in each step are maintained.
This goal can be easily achieved through the use of the same dental forms at various stages of the rehabilitation pathway, facilitating the patient in the process of prosthetic incorporation.
In recent years, there is a growing need to move in the opposite direction of prosthetic simplification as well.
Implant failure, neurodegenerative disease, frailty, and comorbidities highlight the usefulness of using alternatives that are easier to manage and easier to clean, veering toward a solution and implant retention (overdenture) or osteomucosal support.
Better to follow the traditional analog method or make use of CAD-CAM technology?
Find out the benefits and costs in the next article!

